Your cart
No products
-
local_shipping Spend £41,65 to get free shipping
No products
-
Shipping £0,00
-
Total £0,00
Categories
- Great bargains GOLD
- Diamond jewellery
- Gold
- Sterling Silver Jewelry
- Steel jewelry
- Piercing
- Tungsten jewelry
- Titanium jewelry
- Couple pendants
- String necklaces
- Zodiac signs
- Luxurious jewelry
- Ceramic jewelry
- Shamballa
- Magnetic bracelets
- Rubber bracelets
- Leather bracelets
- Bracelets braided
- Key chains
- FIMO jewelry
- Fashion Jewelry
- Wedding rings
- Engagement rings
- Huge Rings
- Gift wrappings
- Watches
- PLAYBOY jewelry
- Jewelry boxes
- Gift ideas
- Stock sale
- Cleaning jewellery
- Our discounts
DIAMOND
A diamond is a transparent crystal of pure carbon. Diamonds are known to have exceptional physical properties, especially hardness and high dispersion of light. With these and other features diamond is highly desired in jewellery and industrial use.
The word diamond is from the ancient Greek word αδάμας, adamas, meaning ‘unbreakable’.
Rough diamond resembles a piece of glass. Only a thorough processing and polishing makes a shining jewel out of untreated raw material. Use of diamond as a decorative jewellery is the best known method dating back to ancient times.

What affects the price of a diamond?
Properties known as ‘4C’:
carat
clarity
colour
cut.
Other physical properties (contents of fluorescent elements), such as the history of the diamond and place of its discovery, colour (blue, green, pink, orange etc.), purity.
Each diamond must have a certificate issued by globally recognized gemmological laboratory. On the certificate (or birth certificate) of a diamond, there must be given information about the 4C - colour, weight, purity and type of cut. The certificate must contain the name and address of the laboratory, the number and date of issuance. Certificate will guarantee the quality and authenticity of your diamond.




Properties
Diamond is the hardest natural material. It retains its glossy surface for a long time even with daily wear. In many countries it is used for gold engagement and wedding rings that are worn every day.
Colour
Light dispersion is a basic characteristic of a diamond and influences its price. Diamonds refract light into all the colours of the rainbow - clear, white, grey, blue, yellow, orange, red, green, pink, brown, or black. This phenomenon of the refraction of light gives the rightly cut diamonds their attractive lustrous appearance. Most diamonds used in jewellery are transparent with a little tint, or they are white diamonds. Pale pink or blue colour tint can already highly increase their price, more intense colouration is usually desirable and diamonds with these colourations are at the highest prices.
Carat
Diamond weight is referred to as carats. One carat is exactly 200 mg. For diamonds weighing less than one carat, a point is used (one hundred points of 2mg).
|
Carats |
Price per carat (US$) |
Total price (US$) |
|
0.5 carat (50 point) |
3,000 |
1,500 |
|
1.0 carat |
6,500 |
6,500 |
|
1.5 carat |
8,500 |
12,750 |
|
2.0 carat |
13,000 |
26,000 |
|
3.0 carat |
17,000 |
51,000 |
|
5.0 carat |
23,000 |
115,000 |
In jewellery a full carat weight is applied when it comes to more than one stone - e.g. in earrings with a single diamond the complete carat weight is used for diamond weight of both earrings together and not separately. It is also used for necklaces, bracelets or similar jewellery.
Clarity
Clarity is the degree of diamond internal defects. These defects may be e.g. foreign material, another diamond crystal or structural irregularities. Diamonds are graded in laboratories according to their clarity. Clear diamonds are very rare. Only 20% of all mined diamonds are clean enough to be used in jewellery; the other 80% is used for industrial needs.
Cut
Diamond cut represents the way it was shaped and polished from its initial form to its final look. There are set mathematical guidelines for the angles and length ratios at which a diamond is to be cut to reflect the greatest amount of light.
Diamond sizes
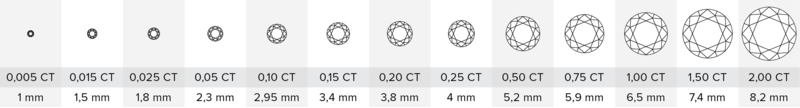
The most popular diamond shapes include:

Quality
Quality of the diamond cut is the most important feature determining beauty of a diamond. A well-honed diamond may seem heavier, clearer and with a nicer tint. The quality of cut is the most important feature, but it is also the most difficult one to assess. A number of factors, including the dimensions, the symmetry and the relative angles rely on the quality of the cut and can influence the characteristics of a diamond. Well-honed diamond should reflect the most light from the top and when viewed from above should look white. Poorly cut diamond looks dark in the centre.
Economic significance
Diamonds have strong economical importance not only as precious stones, but also for its industrial value. Mining, processing and distribution of diamonds is an exclusive and small market. It is dominated by a small number of suppliers. The most famous center for the diamond trade is in Antwerp. The largest exchange with diamonds is in Israel.
Let’s remember that diamonds are gems that symbolize exclusivity, uniqueness and beauty of its owner too.














